AMERICA’S NEWEST HIPSTER HOT SPOT: THE SUBURBS?
by Joel Kotkin 10/09/2014…
 It’s an idea echoed everywhere from “Friends” to “Girls”: Young people want to live in cities. And, we’re told, a lot of them (at least the cool ones) do.
It’s an idea echoed everywhere from “Friends” to “Girls”: Young people want to live in cities. And, we’re told, a lot of them (at least the cool ones) do.
It’s a common assumption. But it’s also wrong.
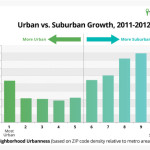
Between 2010 and 2013, the number of 20- to 29-year-olds in America grew by 4 percent. But the number living in the nation’s core cities grew 3.2 percent. In other words, the share of 20-somethings living in urban areas actually declined slightly.
This trend has occurred in supposedly hot cities like San Fransisco, Boston, New York and D.C., notes demographer Wendell Cox. Chicago and Portland, Ore., both widely hailed as youth boom-towns, saw their numbers of 20-somethings decline, too.
To some extent, this is an economic problem. Millennials can’t always afford the most popular cities, which have gotten increasingly expensive and unequal. It doesn’t help that most young people, even with college degrees, are experiencing steadily dropping annual earnings. And theircareers are progressing more slowly too.
But it’s not just that. According to the most recent generational survey research done by Magid and Associates, 43 percent of millennials describe the suburbs as their “ideal place to live,” compared to 31 percent of older generations.
Only 17 percent of Millennials identify the urban core as where they want to settle permanently. Another survey, by the Demand Institute (funded by the Conference Board and Neilsen), found that 48 percent of 20-somethings hoped to move to the suburbs one day. And contrary to popular myth, they hoped to own a single-family home. Sixty-one percent seek more space.
These findings may actually understate the suburban preference. As people age, particularly entering the child-bearing period between 30 and 50, they long have displayed a distinct tendency to move to suburban areas.
And why not?
A lot of the amenities that once drew people to gritty cities are popping up in the suburbs instead.
The New York Times documents a trend of people moving from Manhattan and Brooklyn to the verdant suburbs of the Hudson Valley. Increasingly, those towns boast art house films, vegan restaurants and other hip accoutrements.
Incipient hipster suburbs can also be found in places like Montclair, N.J., Claremont, Calif., and even Irvine, whose Millennial population last decade grew more than four times as much as that of downtown Los Angeles. Once a foodie desert, Irvine and its surrounds now boast dim-sum houses, Vietnamese, Korean, sushi and California cuisine restaurants.
That’s thanks to another trend: Immigrants are bypassing cities and moving to the suburbs in droves, according to Brookings. And they’re bringing good, cheap ethnic food along with them.
Nowhere are these changes more marked than among Asians, now the nation’s largest source of new immigrants. For example, in the New York metropolitan area, the Asian population grew both in numbers and in percentage far more rapidly in the suburbs than in the core city in the past decade. Nationwide, the Asian population in suburbs jumped by almost 2.8 million, or 53 percent, while that in core cities grew 28 percent.
A great American ethnic culinary tour today would take you not to Manhattan, San Francisco, Hollywood or Chicago, but to places like the San Gabriel Valley, roughly 10 miles east of downtown Los Angeles. This highly suburban region of strip malls and giant food palaces arguably boasts the largest, and most diverse, collection of Asian restaurants in the nation.
A CNN survey of America’s top 50 Asian restaurants located seven in the area, the most of any region. That includes foodie havens like New York City. Three others were in the heavily Asian suburbs of Silicon Valley.
As Tyler Cowen noted, the best places to find distinctive ethnic cuisine in Greater Washington is not in the urban core but in far-flung suburban strip malls, where rents are cheap, parking is adequate and there’s a built-in community of eaters craving home.
Much the same can be said for Asian markets, temples or schools. Sugarland, some 22 miles further west of downtown Houston, is home to one of the nation’s largest Hindu temples. The largest Hindu temple in the world is now under construction in Robbinsville, N.J. — an exurb of New York some 60 miles south of Manhattan.
Indeed, in large parts of America, many successful malls are those that are getting “ethnicized.” A prime example is La Gran Plaza on the outskirts of Fort Worth, Tex., where a once-failing mall is now booming, converted to look like an old village in Northern Mexico, with loads of restaurants, markets, wedding and quincenara shops and a huge swap-meet.
This is in addition to live music and, on some Sundays, Catholic Mass.
As their demographics change, so too do the functions of suburbs. No longer mere bedroom communities, they are becoming economic centers of their own. Despite the constant hype about the new appeal of downtown locations, jobs continue to follow the migration of middle-class families. Having been widely written off for dead, suburban office space also began to recover last year at a much quicker rate than in city centers, according to the office consultancy Costar. Overall, suburbs already account for close to three quarters of the nation’s office inventory.
Suburbia is not the city’s antithesis, but its natural extension, particularly as young people morph towards adulthood. Rather than vilify suburbs as fundamentally inefficient, deadening and wasteful, its time to focus on how to improve the preferred environment for work, interaction and raising the next generation for most Americans. Cities have changed too, of course, in many cases for the better. But the suburbs are evolving as well. And all indications suggest that they are likely to retain their preeminence as Americans’ preferred places to settle down.
This piece first appeared at The Washington Post.
Joel Kotkin is executive editor of NewGeography.com and Roger Hobbs Distinguished Fellow in Urban Studies at Chapman University, and a member of the editorial board of the Orange County Register. His newest book, is now available at Amazon and Telos Press. He is author of The City: A Global History and The Next Hundred Million: America in 2050. His most recent study, The Rise of Postfamilialism, has been widely discussed and distributed internationally. He lives in Los Angeles, CA.